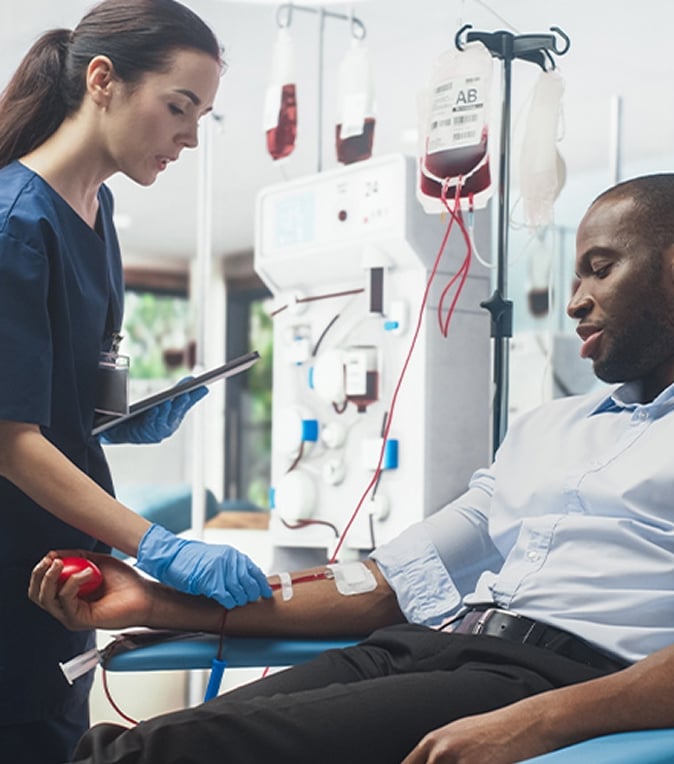
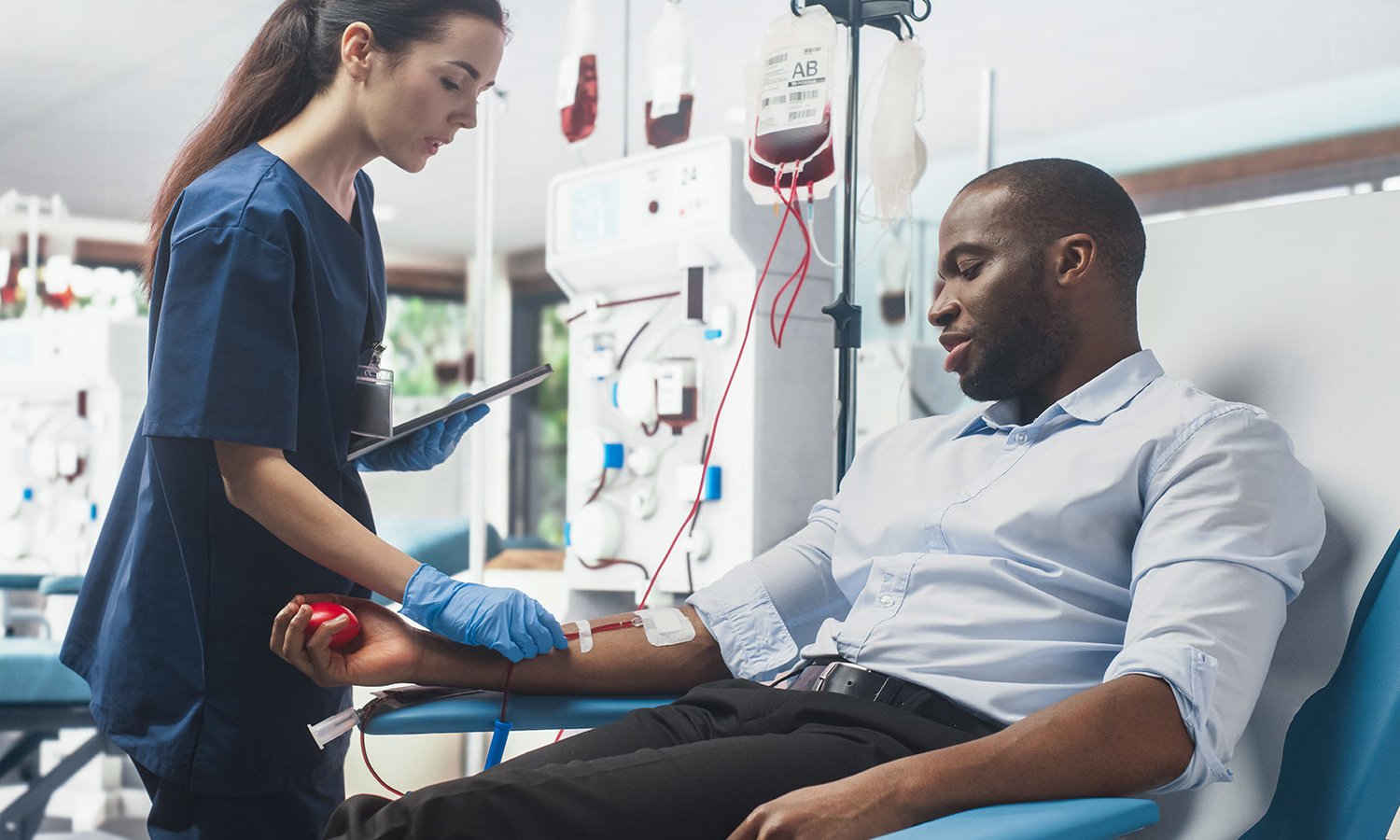
Unmatched Sickle Cell Disease Care in Cleveland
Sickle Cell Disease is a blood disorder inherited from parents who are carriers of the sickle cell gene and is the most common inherited blood disease in the United States. With Sickle Cell, red blood cells are shaped like a half-moon and struggle to move through the blood vessels, causing pain and interfering with oxygen delivery throughout the body. At MetroHealth, we focus on early treatment to prevent lasting damage, and supportive care to decrease pain.
Sickle Cell Disease is common among people of Black, Arab, or Indian descent.
Symptoms include:
- Pain in the joints or sudden chest pain
- Dizziness
- Fatigue
- Difficulty breathing
- Fever
- Swelling of hands and feet
- Frequent infections
- Vision problems, including yellowing of the eye
Preventing lasting damage through early diagnoses
Sickle Cell Disease is diagnosed through a blood test. In the United States, screening is provided at birth, and pediatricians work with hematologists to identify when to begin treatment. It is important to identify Sickle Cell Disease early to decrease infections and prevent organ damage.
Personalized Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
If you have Sickle Cell Disease, it’s important to find the right treatment to limit pain and reduce your risk for stroke or other complications.
At MetroHealth, we provide simple transfusions, partial exchanges, and total exchanges to provide treatment that fits your needs.
MetroHealth can also recommend gene therapy and bone marrow transplant options to treat—and potentially cure—Sickle Cell Disease.
A Lifetime of Support
Sickle Cell Disease must be managed throughout a patient’s life. Our goal is to keep the percentage of sickle cells below 30%, and medication can help once transfusions and exchanges have reduced the amount of crises.
Sickle Cell in the Home
At MetroHealth, we’re dedicated to finding innovative ways to care for you. Through our Sickle Cell in the Home program, hospitalized Sickle Cell Disease patients are discharged 4-8 days early to continue inpatient care and pain management in their own home.
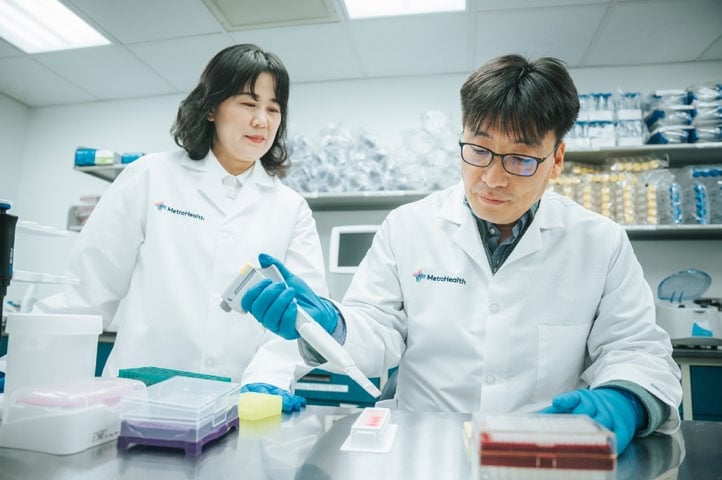
Advancing Care Through Research
At MetroHealth, every oncologist participates in research, bringing advances in cancer care directly to your bedside. We address health disparities by enrolling people from minority populations in clinical trials at more than 4 times the national average.
For more information about our studies, or to enroll in a study that might be right for you, contact our oncology team at 216-77-TREAT.



A Team Dedicated to You
The MetroHealth Cancer Institute team is setting a new standard of cancer care in northeast Ohio. MetroHealth offers unmatched, state-of-the-art, and personalized cancer care.