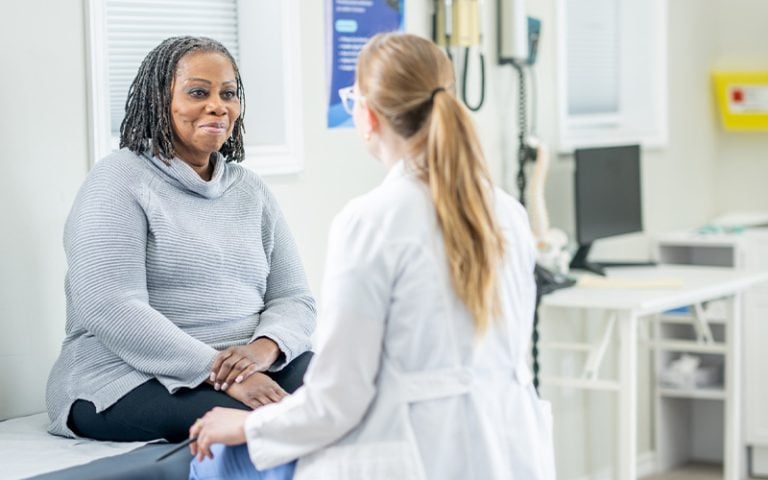
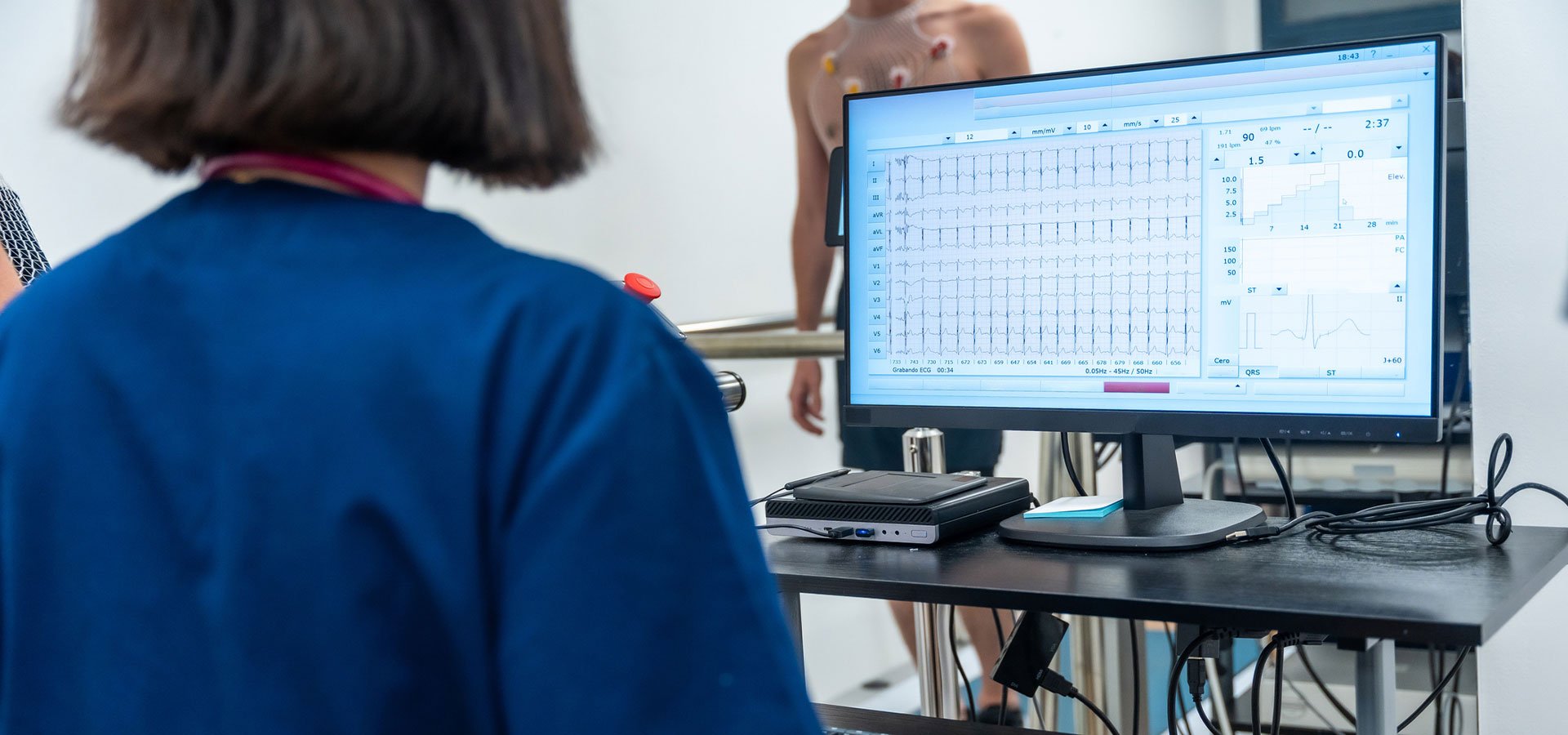
We know your heart.
Electrophysiologists—or EPs—diagnose and treat issues with the electrical impulses in your heart to make sure your heart keeps beating in a normal rhythm.
The Region’s Leader in AFib Treatment
MetroHealth has earned the distinguished American Heart Association’s Get With The Guidelines Gold Award, recognizing our ability to diagnose and treat people with complex atrial fibrillation.

Irregular heart rhythms, often called arrhythmia, means a consistent problem with the rate or rhythm of your heartbeat.
While activity or rest can cause your heart rate to rise and fall, consistently slow, fast or irregular heartbeats prevent your body from getting the blood it needs.
Irregular heart rhythms, left untreated, can cause stroke, heart attacks or heart failure.
MetroHealth’s team of providers can recommend a personalized treatment plan to address your irregular heart rhythm and prevent it from damaging your heart or other important organs.
What can an irregular heart rhythm feel like?
Symptoms include:
- Palpitations
- Flutters
- Fainting
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain or tightness
- Racing heartbeats
- Dizziness
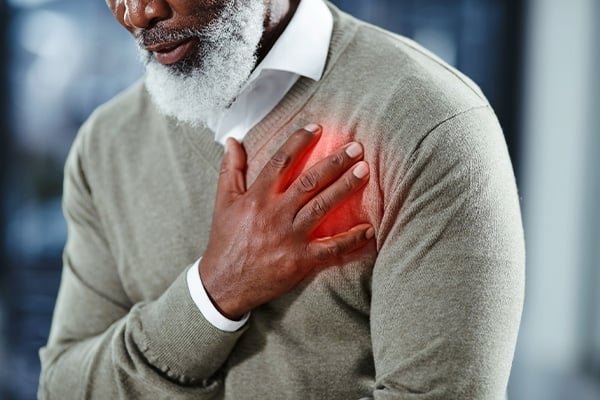

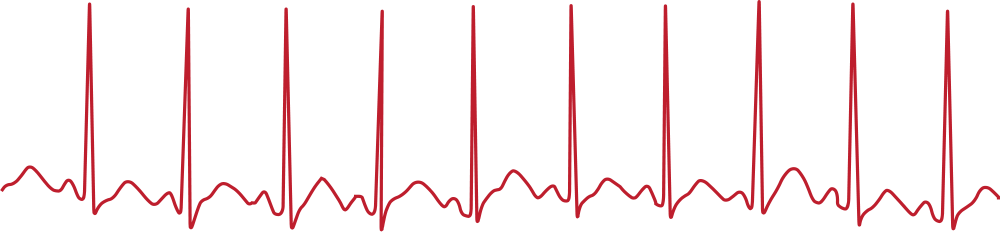
Fast heart rhythms
Called tachycardia, rapid heart rhythms occur when your heart consistently beats at a pace of over 100 beats per minute. While exercise and activity may cause your heart to beat quickly, tachycardia is a fast heartbeat that isn’t consistent with your level of activity.
Tachycardia is often caused by changes in the way the electrical impulses in your heart function.
At MetroHealth, we treat many kinds of tachycardia, including:
- Ventricular tachycardia
- Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT)
MetroHealth is also home to world-renowned providers specializing in the treatment of Long QT syndrome, which causes fast, irregular heartbeats.
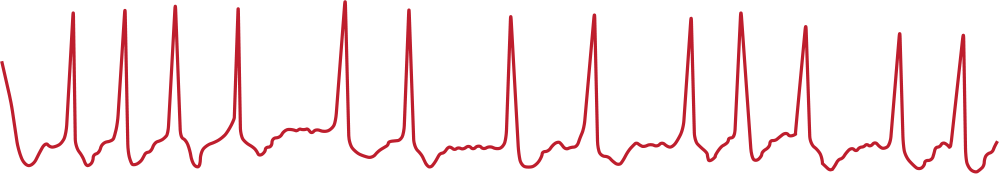
Irregular heart rhythms
Irregular heart rhythms occur when the electrical signals in your heart are misfiring, causing the heart to beat inconsistently.
Atrial fibrillation, or AFib, is the most common type of arrhythmia. AFib occurs when “sick” heart tissue causes rapid and/or irregular beats in the upper chambers of your heart. MetroHealth treats the most complex cases of AFib in our region.
MetroHealth also treats other types of irregular heartbeats, including atrial flutter.
![]()
Slow heart rhythms
Called bradycardia, slow heart rhythms occur when your heart consistently beats at a pace of fewer than 60 beats per minutes. While sleep may cause a low heart rate, bradycardia is a slow heart rate that isn’t consistent with your level of activity.
A bradycardia heart block, also known as atrioventricular block, means your heart’s electrical signals don’t move correctly from your upper chambers to the lower chambers.
Sinus bradycardia is caused by cells in a node in your right atrium—your body’s natural pacemaker—that don’t send electrical signals quickly enough.
Irregular heart rhythms respond well to a range of treatments, but your care will start with one or more tests to help us understand the type of irregular heart rhythm you have, as well as your treatment options.
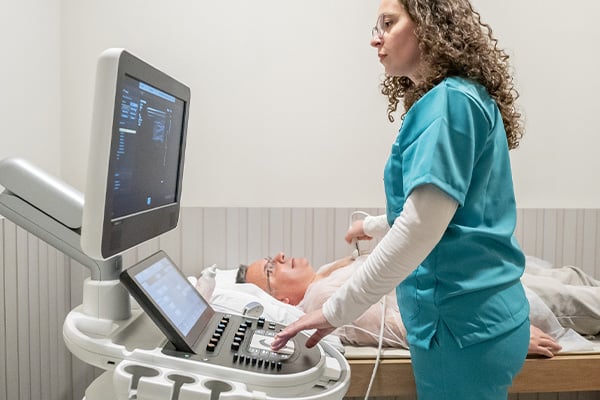
Tests may include:
- An electrocardiogram, often called an EKG or ECG. In this test, we’ll place sensors—called electrodes—on your chest to record the electrical activity in your heart. This tests shows your heart rate and rhythm and can identify heart damage.
- If your irregular heart rhythm symptoms come and go, a one-time electrocardiogram may not capture your arrythmia. In that case, we’ll have you use a portable device at home—either a Holter monitor or event monitor—to help us understand what is happening when you feel symptoms.
- Echocardiograms use an ultrasound machine to show the size and structure of your heart and chambers, allowing us to see if your heart function and structure is causing an issue. In an echocardiogram, we can also see how your heart valves are working and how blood moves within your heart.
- An EP study—or electrophysiology study—is a more invasive outpatient test where thin tubes are placed inside different areas of your heart, through blood vessels. Sensors on the ends of the tubes records your heart’s electrical activity to detect which part of your heart is causing arrhythmia. Often, EP studies are done prior to ablation treatment, which prevents irregular electrical signals.
Once we are able to discuss your symptoms and the result of any diagnostic testing, our team of providers can help develop a personalized treatment plan to address your irregular heart rhythm.
Sometimes, if your symptoms are under control and testing reveals that your condition is not causing damage, our team will continue to monitor you without treatment.
Often, the first step in treatment is medication intended to make your heart rhythm more regular.
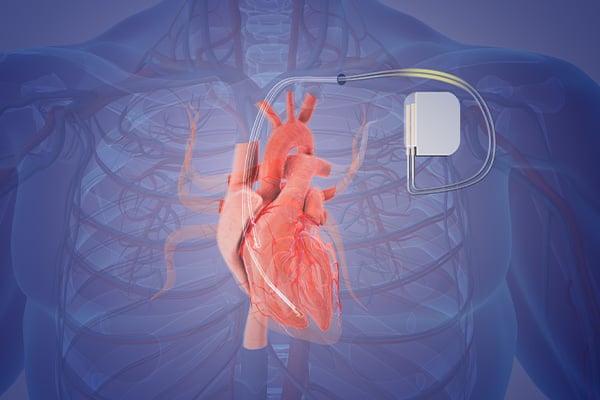
Other treatments include:
- Ablation, where heat is used to create scar tissue on malfunctioning tissue in your heart to prevent abnormal electrical signals that are causing AFib. Pulmonary vein isolation, or PVI, is a type of ablation.
- Watchman, a small device implanted via a minimally-invasive procedure in your left atrial appendage to prevent stroke-causing blood clots as a result of AFib.
- Defibrillators, including implantable cardioverter defibrillators that can provide electrical stimulus to your heart to keep it beating when a fatal irregular heartbeat is sensed.
- Pacemakers, a small device that keeps your heart beating at a regular pace.
A team dedicated to you.
The MetroHealth Heart and Vascular Center is setting a new standard of care in northeast Ohio.